|
|
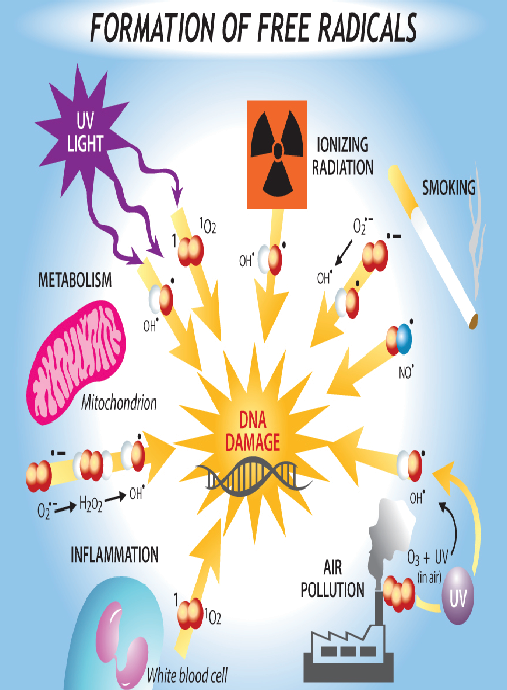 |
What are Free Radicals (Oxidative stress) ?
In very simple terms, a free radical is an atom with an “unpaired electron’. This atom is called a free radical and is “very reactive” in that it tries to stabilize itself by seeking out another electron from another otherwise stable atom with “paired electrons”. This action results in a “Chain reaction” and that is when “excessive free radical activity occurs”.
What do the Free Radicals do?
Free radicals destroy cells by damaging their membranes. Your body needs free radicals to function and as a defense mechanism. Free radicals are used to metabolize glucose and fat and to destroy invading harmful bacteria and viruses. A burst do free radicals is used to destroy the cells of theses invading bacteria and viruses to kill them. The body also uses free radicals to destroy cancer and other abnormal cells. However, it is when there is excessive free radicals that it causes health problems for the body. The excess free radicals then attack the healthy cells of the body causing aging and other degenerative diseases, which is called ‘Oxidative Stress’
|
|
How can Free Radicals be measured?
MDA(Malondialdehyde) is a byproduct produced when free radicals oxidize fat. MDA is used as a standard measurement for oxidation level damaged by free radical. It is therefore important to regularly check and monitor the free radical activity in the body and it can be done using with FREE RADICHECK test strips.
Affixed to each firm plastic strip are two reagent areas that test for MDA and Creatinine in urine. Measurement of the two tests at the same time from a random single-void urine sample allows for determination of the MDA(Malondialdehyde) to Creatinine ratio (ACR).
|
|
|
| Other comments to reduce oxidative stress |
|
Get a balanced diet, consume adequate amount of fresh fruits and vegetables (organic foods are preferred), drink much fresh water and avoid fatty, fried, and processed foods.
Avoid excessive consumption of sugar and salt (choose natural or less refined ones when to use)
Consume more oxidant-rich tea (green tea) and fruits, but drink less coffee
Do some enough and regular base exercise in the fresh air. But, refrain from extreme exercise (this will increase oxidative stress level)
Keep away from pollution, cigarette smoke, and toxic materials
Take enough and regular sleep
Take enough rest with a physical and mental relax.
|
| Diseases to be caused by Free Radicals |
|
- Aging acceleration
- Cancers, e.g. Cervical cancer, Ovarian cancer, Liver cancer etc.
- Inflammation, e.g. Arthritis, Atopic Dermatitis etc.
- Diabetes
- Neurodegenerative diseases, e.g. Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson´s disease etc.
- Cardiovascular disease, e.g. Stroke, Arteriosclerosis, High blood pressure etc.
- Kidney disorders
- Respiratory diseases, e.g. Influenza etc.
|
| Reference |
|
- Stability and Intra-Individual Variation of urinary Malondialdehyde and 2-Naphthol J Prev Med Public Health 2008;41(3):195-199
- A review of recent studies on malondialdehyde as toxic molecule and biological marker of oxidative stress. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2005;15(4):316-328
- Evaluation of a simple colorimetric analysis for urinary malondialdehyde determination. Pathology and Laboratory Medicine International 2010:2 23-26
- Importance of lipid peroxidation biomarkers and methodological aspects for malondialdehyde quantification. Quim Nova. 2009;32;169-174
- Diabetes,oxidative stress and physical exercise. J Spots Science and Medicine (2002) 1, 1-14
|
|


