Drug Adulteration Test
본문

![]() Test strip for checking foreign substances added directly to a urine specimen to prevent the detection of drug use
Test strip for checking foreign substances added directly to a urine specimen to prevent the detection of drug use
| Measurement Item | Creatinine, Nitrite, Glutaraldehyde, pH, Specific Gravity, Bleach, PCC |
|---|---|
| Testing Method | Dipstick / Semi-quantitative / Colorimetric |
| Reaction Time | 60 sec |
| Storage | 2~30℃ |
| Shelf Life | 24 months |
Why is the Urine Adulteration Test performed?
People try to undermine their drug tests by adding adulterants to their urine specimens.
Several adulterants can cause false negative results in drug tests by interfering with the screening immunoassays.
Result Interpretation
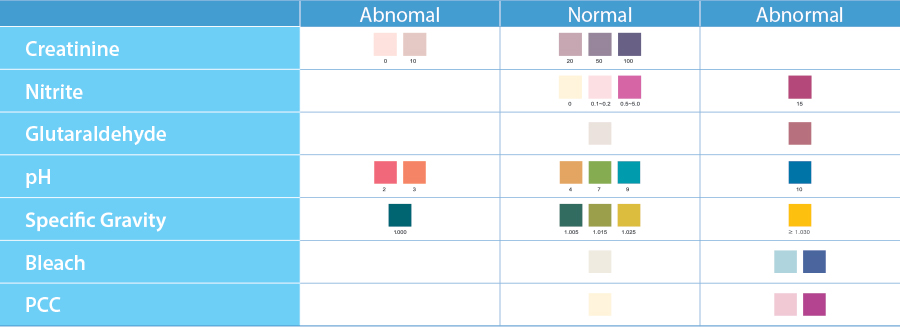
Creatinine
Low creatinine levels may indicate dilute urine.
The absence of creatinine (‹20 mg/dl) is indicative of a specimen not consistent with human urine.
Nitrite
tests for commonly used commercial adulterants such as "Klear" or "Whizzies".
They work by oxidizing the major cannabinoid (marijuana) metabolite THC COOH².
Normal urine should contain no trace of nitrites.
Positive results generally indicate the presence of an adulterant.
Glutaraldehyde
Glutaraldehyde is not normally found in urine.
Adulterants such as UrinAid and Clear Choice contain glutaraldehyde which may cause false negative screening results by disrupting the enzyme used in some immunoassay tests.
pH
Normal pH levels should be in the range of 4.0 to 9.0. Values outside of this range may indicate sample tampering.
Specific Gravity
Values outside the normal range of 1.005 to 1.025 may be the result of specimen dilution or adulteration.
Bleach
Normal human urine should not contain Bleach.
PCC
Normal human urine should not contain PCC.